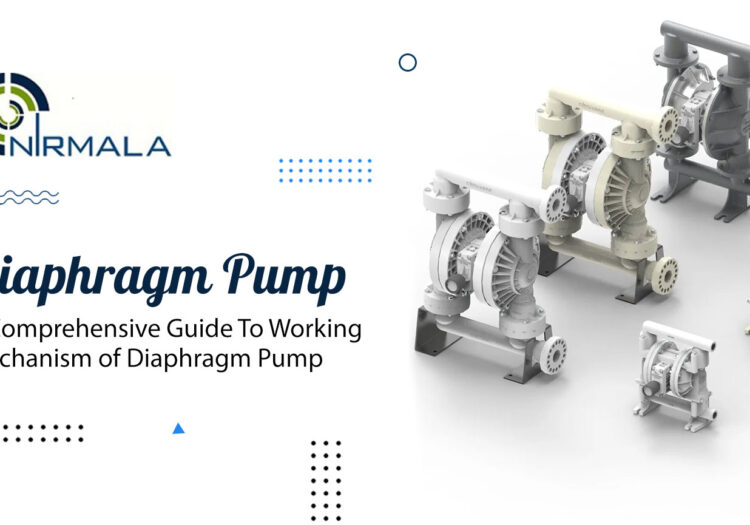
Diaphragm Pump has many uses and can process many fluids, making them highly marketable. This type of pump is classified as a positive displacement pump since the flow rate does not change drastically with pump discharge. These pumps can move fluids with various viscosities and solids concentrations.
Since they can be made with multiple body materials and diaphragms, pumps are well-suited for handling aggressive chemicals, including acids. The purpose, construction, and uses of pumps are covered here.
The Diaphragm Pump: What Is It?
Known as a PD pump or positive displacement pump, a Diaphragm Pump is one such device. A membrane pump is another name for it. Blending the reciprocating action of a rubber, Teflon, or thermoplastic diaphragm and appropriate valves on any face of the diaphragm, this pump can propel liquid.
These pumps are commonplace in various settings, as they may be used to process multiple fluids. These pumps are versatile and able to move fluids of varying viscosities. Since they can be constructed using a variety of diaphragms and body materials, they are also helpful in dealing with numerous corrosive compounds like acids.
Diaphragm Pumps: How They Work
To receive and expel liquid, a double pump employs two flexible diaphragms that respond back and forth to create a temporary hall. The air displacement principle, considered a partition between the air and the fluid, is the basis for the pump’s operation.
Diaphragm Pump Performance Traits
The suction lift capabilities of pumps supplied by Diaphragm Pump suppliers in India are well-known. The chamber and diaphragms’ size and rate determine the pressure and flow rates. Regarding slurries and sludges, pumps are your best bet. Their maximum discharge pressure is 1200 bars.
Because of how they’re made, they perform admirably even when utterly devoid of water. They are employed to make artificial hearts due to their resemblance to natural heart function. They can be as efficient as 97% when properly primed and are self-priming in most cases. As long as they aren’t small, they can handle the most viscous liquids on the market.
Applications of Diaphragm Pump
Due to their adaptability, Double Diaphragm Pump can be found in practically every field where fluid transmission is necessary. They find widespread application as a means of dewatering or water removal in various commercial settings. Their efficiency and precision make them useful for filling, dispensing, and measuring.
They are commonly used in filter press applications due to their high-pressure output, which is helpful for spraying and cleaning.
Benefits of Diaphragm Pump
These are some of the benefits of using a pump:
- Self-priming;
- Explosion-proof;
- Variable Flow Rate and Expulsion Pressure;
- Portability;
- Ease of Installation;
- Longevity of Operation;
- Energy-Efficient;
- Pumping Chemicals and Other Harmful Fluids;
- Overcoming Standing Force in a Flow Line;
- Self-Priming;
- Explosion-proof;
- Variable Flow Rate and Expulsion Pressure;
- Portability;
- Easy Installation.
Conclusion
Nirmala pumps and Equipments has become one of most prominent Diaphragm Pump Manufacturers in India. Due to our dedication to 100% client satisfaction, we can maintain a competitive edge in the marketplace. We can build trustworthy partnerships with our clients and earn their continued patronage by always doing what is right.

Nirmala Pumps & Equipments
Nirmala Pumps & Equipments is an Indian company that manufactures and supplies pump systems, valves, strainers, and pneumatic pumps since 1989. We provide services to different industries, both domestically and internationally, such as citrus, distilling, wastewater treatment, and petroleum.